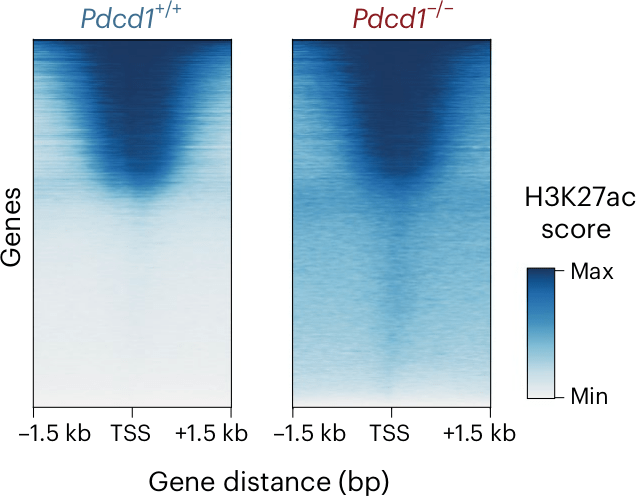
PD-1 is a critical tumor suppressor in T cells. Loss of PD-1 in T cell lymphomas results in higher activity of ATP citrate lyase and higer levels of extramitochondrial acetyl-CoA. This allows hyperacetylation of H3K27 in the context of AP-1 transcription factors. Pharmacological inhibition of ATP citrate lyase can counteract aberrant AP-1 activity and is toxic in these cancers.
Happy that we could contribute our expertise in chromatin analyses.
published in Nature Cancer