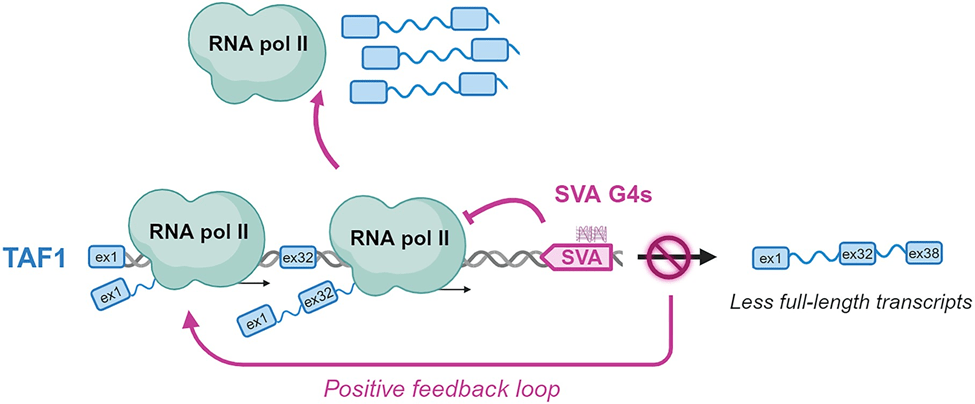
G-quadruplexes (G4s) are non-canonical nucleic acid structures that form in guanine-rich regions and play a significant role in regulating the TAF1 gene in X-linked dystonia parkinsonism (XDP). In this condition, a retrotransposon called SVA is inserted into intron 32 of the TAF1 gene, promoting the formation of stable G4s. These G4 structures hinder the proper transcription of TAF1, leading to decreased full-length TAF1 transcripts downstream of the insertion site and abnormal gene expression. Stabilizing or destabilizing these G4s significantly alters TAF1 transcription, opening possibilities for therapeutic intervention.
Great collaboration with Sara Richter lab!
published in Nucleic Acids Research